Interacting with GPT and External Tools for Information Retrieval
Imagine you’re chatting with an AI model, say ChatGPT, and you ask it, “Who won the NBA championship this year?” You might expect an immediate and accurate answer, but there’s a catch. The training data for ChatGPT only extends up to September 2021, and it doesn’t know anything about the world after that. So, it might either make a guess based on the data it was trained on or tell you that it doesn’t know.
But what if there was a way for ChatGPT to access up-to-date information and provide accurate answers even to questions about recent events? This is where the interaction between AI agents, like LangChain, and external tools, such as Wikipedia, comes into play. In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into how LangChain uses these tools to retrieve external information and how it interacts with GPT.
The Basics: GPT and LangChain
GPT is a transformer-based language model developed by OpenAI. It’s trained on a vast corpus of text data and can generate coherent and contextually relevant sentences. However, GPT doesn’t inherently have the capability to interact with external databases or tools.
This is where an AI agent like LangChain comes in. LangChain can load various tools, including Wikipedia, and use them to retrieve external information. The agent interacts with GPT, providing it with the necessary information to generate responses.
The Interaction Process
Let’s break down the interaction process between the AI agent, GPT, and an external tool like Wikipedia.
Step 1: User Query
The process begins with a user query. For example, a user might ask, “Who won the NBA championship this year?”
Step 2: GPT Processing and Decision to Use External Tool
The AI agent sends this query to GPT. GPT processes the query and generates a response. However, if the information isn’t within GPT’s training data, it may not be able to provide an accurate answer. In such cases, GPT might suggest an action, such as looking up the information on Wikipedia.
The action suggestion is a critical part of the process. It’s facilitated by an additional model that’s trained to recognize when an external action is needed. This model, often a reinforcement learning model, is trained on a dataset where the correct actions are provided. The model learns to recognize the situations where an external action, like a database lookup, is beneficial.
The training process involves providing the model with rewards and penalties based on its decisions. If the model correctly identifies a situation where an external action is needed, it receives a reward. If it fails to do so, it receives a penalty. Over time, the model learns to make accurate decisions about when to suggest an action.
Based on GPT’s suggestion or its own decision-making algorithms, the AI agent decides to use an external tool to retrieve the necessary information. In our example, the agent might decide to use the Wikipedia tool to look up the NBA championship.
Step 3: Interaction with External Tool
The AI agent interacts with the Wikipedia tool, sending a request to retrieve the relevant information. The Wikipedia tool processes this request, searches its database, and returns the information.
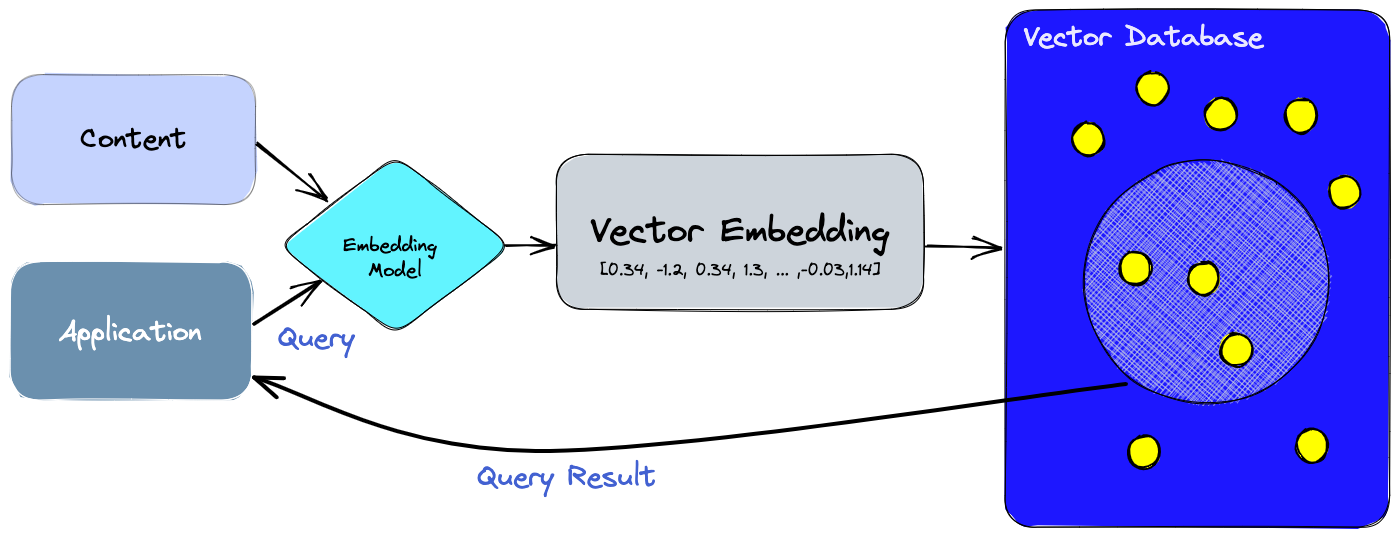
The Wikipedia tool uses a vector database to process the request. A vector database is a type of database that uses vectors, or mathematical objects that have magnitude and direction, to represent data. This allows for efficient and accurate searching of large amounts of data.
For example, the Wikipedia tool might convert the query “NBA championship” into a vector using a process called vectorization. This vector is then compared to the vectors of all the articles in the Wikipedia database. The comparison is done using cosine similarity. The article/paragraph with the highest cosine similarity to the query vector is considered the most relevant and is returned as the result.
Step 4: Processing the Retrieved Information
The AI agent receives the information from Wikipedia. It then processes this information and prepares it to be sent to GPT. This might involve formatting the information or extracting the relevant parts.
For example, the AI agent might extract the relevant sentence, such as “The Denver Nuggets are the winners of the 2023 NBA championship,” and format it to “Answer the question on the basis of the following information. The Denver Nuggets are the winners of the 2023 NBA championship.” send this to GPT.
Step 5: GPT Generates the Final Response
The AI agent sends the retrieved information to GPT. GPT processes this information and generates the final response. In our example, GPT might generate a response like, “The Denver Nuggets are the winners of the 2023 NBA championship.”
Step 6: User Receives the Response
Finally, the AI agent sends GPT’s response to the user. The user receives the accurate answer to their query, even though the information wasn’t within GPT’s training data.
Implementing the Process with LangChain
With LangChain, implementing the above steps is straightforward. Here’s a code example.
When we do not interact with external sources:
import os
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = "XXXXXX" # Put your own openai api key here
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
prompt = "Which team is the winner of NBA 2023?"
Output:
It is impossible to predict the winner of the NBA 2023 season at this time.
When we load the Wikipedia tool:
import os
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.agents import load_tools, initialize_agent
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = "XXXXXX" # Put your own openai api key here
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
prompt = "Which team is the winner of NBA 2023?"
tools = load_tools(["wikipedia"], llm=llm)
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent="zero-shot-react-description", verbose=True)
agent.run(prompt)
Output:
> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
I need to find out who won the NBA championship in 2023
Action: Wikipedia
Action Input: NBA 2023
Observation: Page: 2023 NBA Summer League
Summary: The 2023 NBA Summer League (branded as NBA 2K24 Summer League 2023 for sponsorship reasons) is the off-season competition held by the National Basketball Association (NBA) primarily at the Thomas and Mack Center and Cox Pavilion in Las Vegas, Nevada on the campus of University of Nevada, Las Vegas from July 7 to 17, 2023. The summer league consisted of the California Classic, Salt Lake City Summer League, and the Las Vegas NBA Summer League.
Page: 2023 NBA Finals
Summary: The 2023 NBA Finals was the championship series of the National Basketball Association (NBA)'s 2022–23 season and conclusion to the season's playoffs. The best-of-seven playoffs was played between the Eastern Conference champion Miami Heat and the Western Conference champion Denver Nuggets. The series started on June 1, and concluded in a Denver victory on June 12.The Nuggets defeated the Heat in four of five games, winning their first championship in franchise history after 47 seasons in the NBA. Denver's Nikola Jokić was unanimously voted the NBA Finals Most Valuable Player (MVP), after averaging 30.2 points, 14.0 rebounds, 7.2 assists, and 1.4 blocks while shooting 58.3% from the field and 42.1% from the 3-point line. Jokić is the lowest-selected player to ever win Finals MVP, being the 41st pick of the 2014 NBA draft. This marked the first NBA Finals appearance for Denver. This was also the second Finals to feature a No. 8 seed, along with the 1999 NBA Finals.
Page: 2023 NBA playoffs
Summary: The 2023 NBA playoffs was the postseason tournament of the National Basketball Association's 2022–23 season. The playoffs began on April 15 and concluded on June 12 with the Denver Nuggets winning the 2023 NBA Finals.
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: The Denver Nuggets are the winners of the 2023 NBA championship.
> Finished chain.
The Denver Nuggets are the winners of the 2023 NBA championship.
The interaction between an AI agent, GPT, and external tools like Wikipedia opens up a world of possibilities. It allows us to leverage the power of GPT’s language generation capabilities and combine it with the vast information available in external databases. This synergy, facilitated by sophisticated machine learning models and mathematical techniques, enables the creation of AI systems that can answer a wider range of queries and perform more complex tasks, bringing us one step closer to truly intelligent machines.